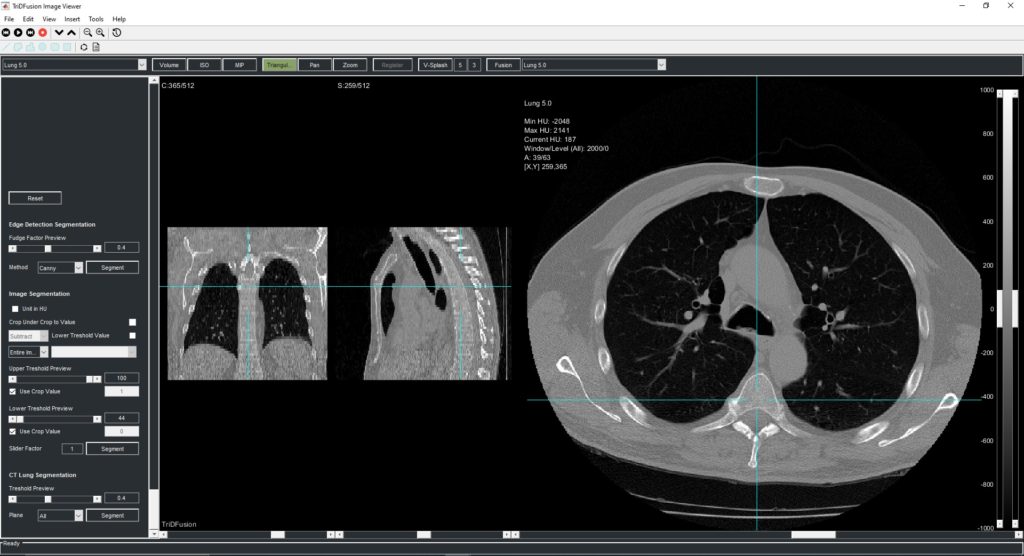
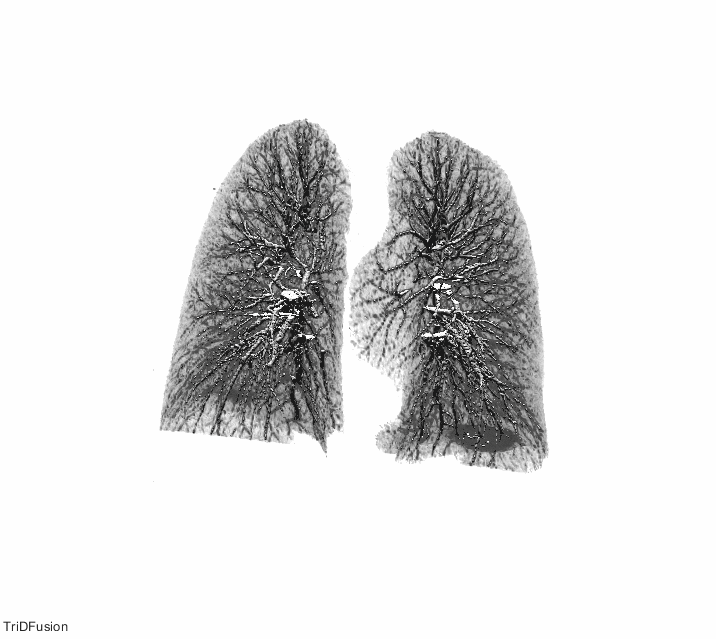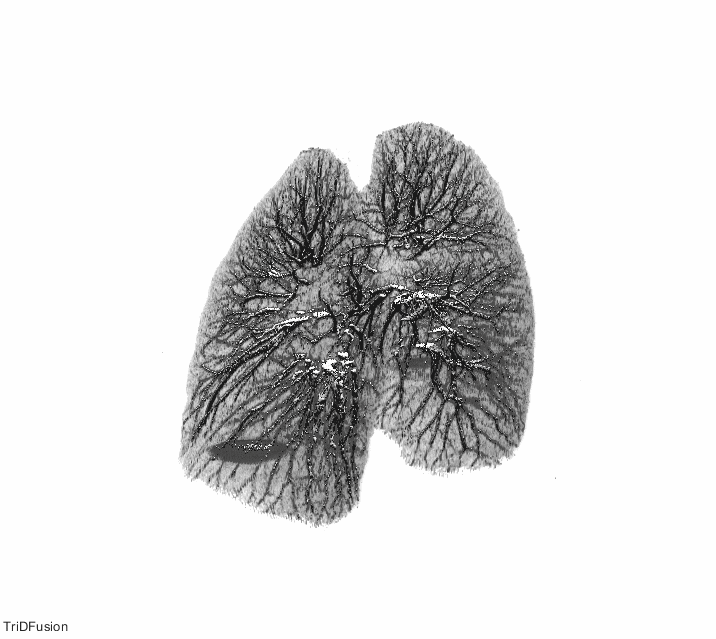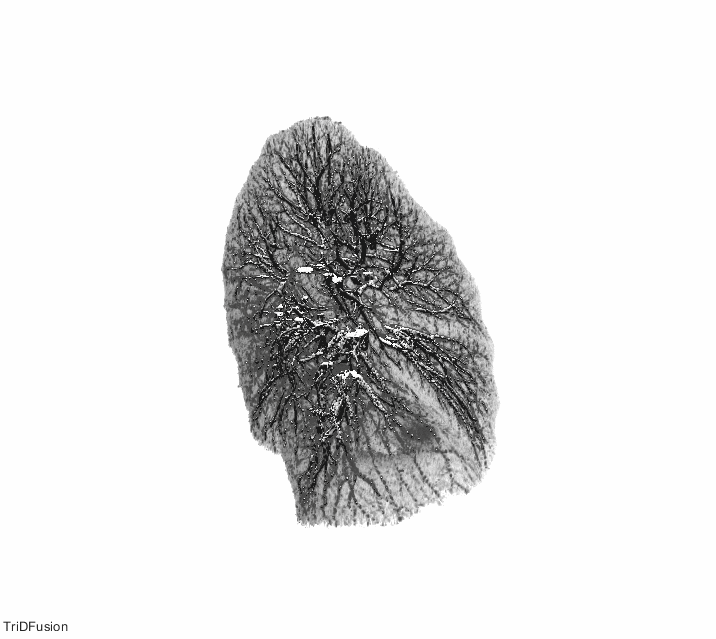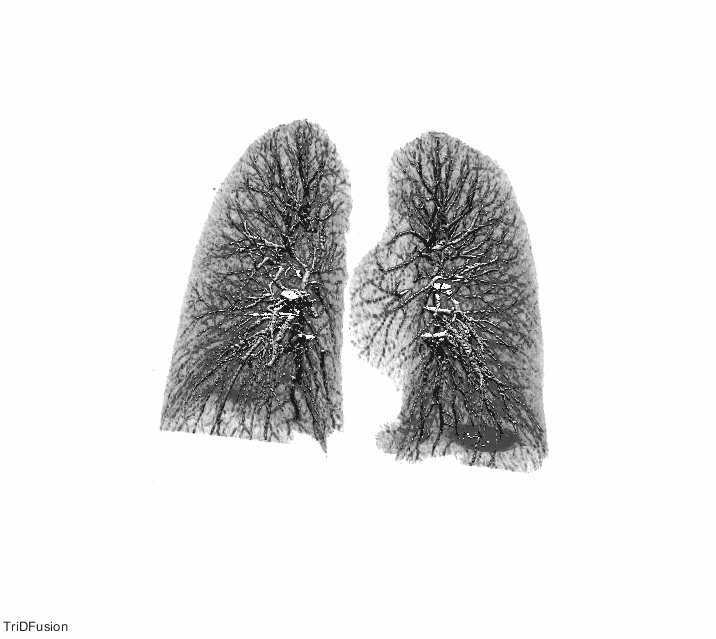
The TriDFusion (3DF) Lung Segmentation algorithm in MATLAB first preprocesses the image by removing noise, enhancing contrast, and normalizing the intensity values. The image is then segmented using a thresholding method to separate the lung region from the surrounding tissue.
The strel method is then applied to the segmented image to remove the airways and blood vessels, which can interfere with accurate lung segmentation. The strel method involves applying a structuring element, which is a mathematical morphology operator, to the image to remove unwanted structures while preserving the lung region.
After applying the strel method, the algorithm uses mathematical models and morphological operations to refine the segmentation and improve the accuracy of the lung boundary delineation. The algorithm also includes a lung fissure detection method that identifies the fissures that separate the different lobes of the lung, allowing for more accurate and precise segmentation.
Once the segmentation is complete, the TriDFusion (3DF) Lung Segmentation algorithm in MATLAB generates a 3D representation of the segmented lungs, which can be used for various applications such as tumor detection, ventilation-perfusion analysis, and radiation therapy planning.
The TriDFusion (3DF) Lung Segmentation algorithm in MATLAB and strel method provides an efficient and accurate way to segment the lungs from medical images, reducing the time and effort required for manual segmentation while improving the accuracy of the segmentation results.